Multi-Agent vs Single-Agent Systems: Unlocking AI's Full Potential
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved into a diverse and complex ecosystem of intelligent entities capable of learning, decision-making, and automation. Among the foundational paradigms shaping the AI landscape are single-agent systems and multi-agent systems. As businesses and industries increasingly integrate AI for automation and optimization, understanding the distinction between these two models is essential. This blog delves deep into the multi-agent vs single-agent debate, exploring their architectures, advantages, limitations, and how each can unlock AI's full potential.
What Are Single-Agent Systems?
Single-agent systems are AI frameworks in which a lone agent interacts with an environment to achieve specific goals. This agent senses the environment, processes data, and makes decisions independently, often optimizing for one objective or a set of closely related tasks.
Key Characteristics of Single-Agent Systems:
- Autonomy: Acts independently without reliance on other agents.
- Centralized Control: Decision-making is streamlined within one agent.
- Deterministic Interaction: Operates in an environment where outcomes depend solely on the agent's actions.
- Simplified Architecture: Easier to design, develop, and test.
Use Cases:
- Robotic vacuum cleaners
- Personal AI assistants (e.g., Siri, Google Assistant)
- Game AI for single-player games
- Rule-based financial trading bots
Although single-agent system are simple and work well, they become much harder to use when situations become complicated or involve many participants.
What Are Multi-Agent Systems?
Multi-agent systems (MAS) bring together many intelligent agents that all interact with each other and their environment. These agents are able to coördinate, battle or coexist to deal with problems that are too tough for one agent or are intrinsically distributed.
Key Characteristics of Multi-Agent Systems:
- Decentralized Control: Each agent operates semi-independently.
- Communication and Coordination: Agents often share information and synchronize activities.
- Scalability: Easily extended with more agents.
- Adaptability: Suited for dynamic and unpredictable environments.
Use Cases:
- Autonomous vehicle coordination
- Smart grid energy management
- Supply chain optimization
- Distributed robotics (e.g., drone swarms)
- AI-powered multiplayer gaming
The attraction of autonomous multi-agent systems is due to their adaptability, solid design and ability to show how entities in the world work together.
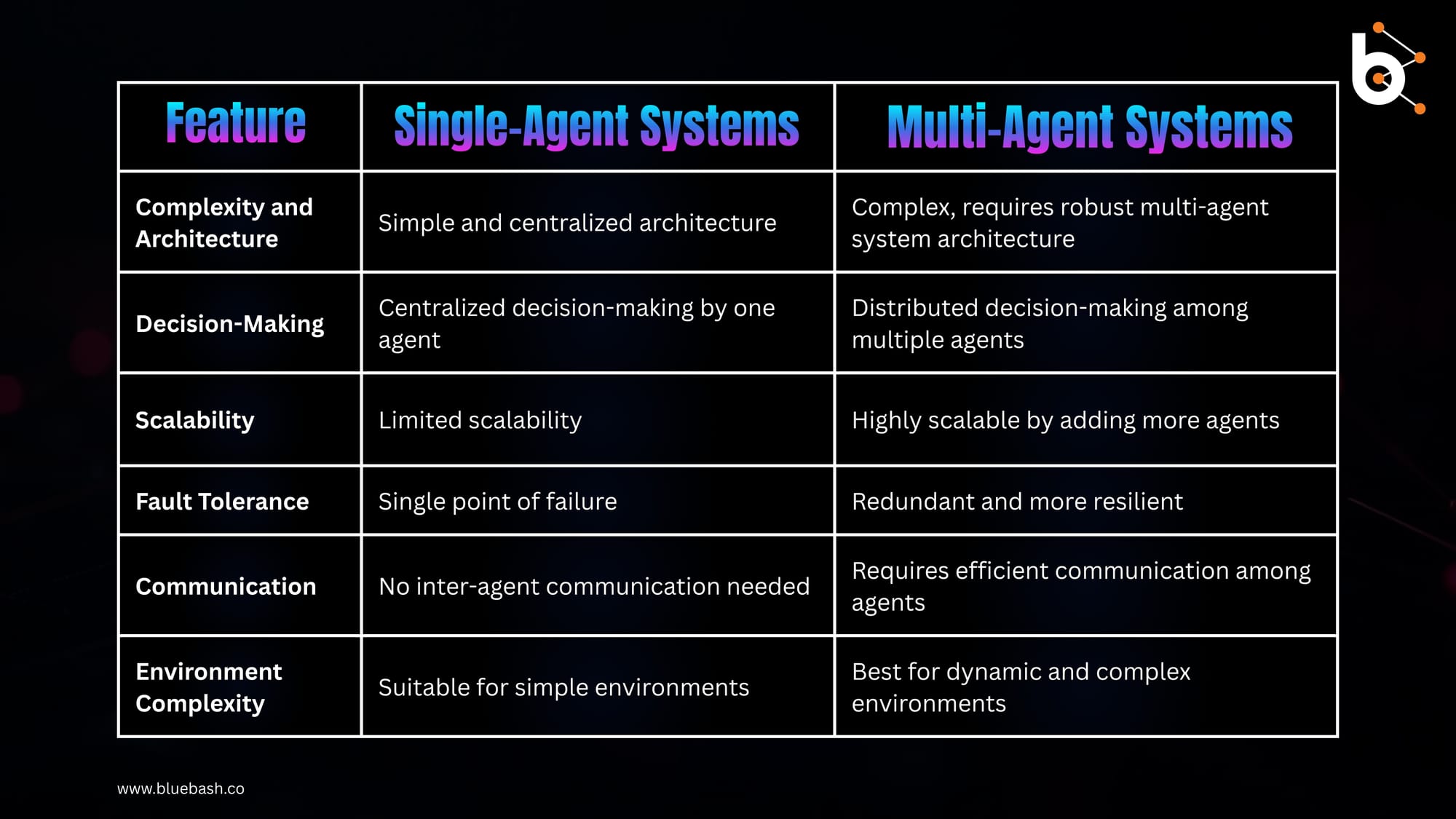
Multi-Agent vs Single-Agent: Key Differences
When to Choose Single-Agent Systems
- The problem is straightforward and well-defined.
- Only one agent is needed to achieve the desired result.
- Communication overhead must be minimized.
- Real-time performance in controlled environments is a priority.
For example, a smart thermostat optimizing a single room's temperature doesn't need a fleet of agents. A well-trained single-agent system is ideal here.
When to Choose Multi-Agent Systems
- Tasks are distributed across locations or functions.
- The environment is dynamic, requiring collaboration or competition.
- Scalability and flexibility are crucial.
- The problem involves coordination, negotiation, or collective decision-making.
Use cases like warehouse automation or drone delivery require an AI multi-agent system to coordinate paths, avoid collisions, and manage load-balancing effectively.
Implementation of Multi-Agent Systems
Building a multi-agent system involves several key steps, often centered around a central orchestrator that manages agent interactions. Let’s look at how this works using the LangGraph framework as an example.
Steps to Implement a Multi-Agent System
- Define Agents: Each agent is assigned a specific role and maintains a unique state.
- State Management: Persistent variables track activities and decisions, ensuring continuity.
- Conditional Routing: A router dynamically determines the flow of information between agents.
- Workflow Execution: A workflow object orchestrates the sequence of agent interactions.
This architecture ensures seamless communication and coordination among agents, enabling efficient task execution. The design of agent-based systems in AI plays a crucial role in achieving these outcomes, particularly in ai multi-agent systems.
Advantages of Multi-Agent Systems
- Enhanced Problem Solving
When tasks can be divided, multi-agent systems outperform single-agent counterparts by parallelizing efforts and integrating diverse perspectives. - Real-World Modeling
They more accurately simulate environments like human societies, business ecosystems, or biological systems, making them essential for agent-based systems in AI. - Flexibility and Modularity
New agents can be introduced with specific capabilities without disrupting the entire system. This makes MAS ideal for custom AI agents tailored to unique business needs. - Improved Resilience
With no single point of failure, MAS are inherently more robust and fault-tolerant.
Real-World Applications: MAS in Action
- Autonomous Vehicles
It is important for self-driving cars at intersections to talk and match their movements to keep accidents and traffic jams from occurring. A multi-agent system is used to design the teamwork between these agents. - Smart Grids
Power generation and consumption units act as agents adjusting supply and demand. MAS optimizes energy distribution efficiently. - Healthcare Systems
In hospital management, different AI agents can manage patient data, diagnostics, and staff scheduling collaboratively. - E-commerce and Logistics
An inventory manager, customer service bot and delivery drone function in a multi-agent system, helping to improve how things are operated.
These examples underscore the growing reliance on autonomous multi-agent systems in next-generation digital solutions.
Why Choose Bluebash for Your AI Agent Needs?
At Bluebash, we understand that every AI implementation must align with the specific needs, goals, and environments of your business. Whether you're seeking a single-agent system for streamlined tasks or a robust multi-agent system to manage distributed operations, we offer end-to-end solutions that ensure performance, security, and scalability.
Here's why businesses choose Bluebash:
- Expertise in Agent-Based AI Systems: Our team specializes in designing both single and autonomous multi-agent systems, tailored for a wide array of industries.
- Custom AI Development: From ideation to deployment, we provide custom AI agents that address unique challenges with precision.
- Scalable Architecture Solutions: Whether it’s a simple tool or a complex multi-agent system architecture, we build solutions that grow with your needs.
- Collaborative Approach: We work closely with your team to ensure integration and functionality meet operational goals.
- End-to-End Support:We ensure your succeed by giving continuous maintenance, updates and keeping everything optimized.
With our proven track record in AI agents development solutions, Bluebash is your ideal partner in unlocking the full potential of AI-driven automation and intelligence.

Future of AI with Multi-Agent Systems
As AI matures, we are likely to see a shift toward multi-agent systems in increasingly complex scenarios. The collaborative intelligence enabled by MAS is key to developing next-gen AI capabilities such as:
- Decentralized finance platforms
- Autonomous smart cities
- AI governance and ethical decision-making frameworks
- Space exploration and robotics swarms
The drive toward custom AI agents designed for specific roles within a MAS will also grow, giving organizations the ability to finely tune performance across departments or industries.
Conclusion: Unlocking AI's Full Potential
Choosing between single-agent systems and multi-agent systems ultimately depends on your specific business objectives, system complexity, and scalability needs. A single agent can handle simple tasks easily, but when tasks are collaborative and must be able to adapt, multi-agent models achieve better results.
At Bluebash , We work together to supply extremely detailed technical guidance and wise insights on AI matters, so that your use of AI truly benefits your business. If you want to begin simply or use advanced AI applications, Bluebash helps your venture remain practical, flexible and adapted for the future.
FAQ's
- What is the key difference between single-agent and multi-agent systems?
Single-agent systems have one AI entity operating independently, while multi-agent systems involve multiple agents that coordinate or compete within a shared environment. - When should I choose a single-agent system?
Choose single-agent systems for straightforward, isolated tasks with minimal collaboration needs and where system simplicity is a priority. - What are the benefits of multi-agent systems?
They offer scalability, flexibility, and resilience, making them ideal for dynamic environments and tasks requiring distributed collaboration. - How do multi-agent systems coordinate effectively?
They use communication protocols, centralized or distributed routing, and shared data states to synchronize decision-making and actions. - Why should I choose Bluebash for agent-based AI solutions?
Bluebash provides custom AI development, scalable architectures, and end-to-end support, ensuring tailored solutions for both single and multi-agent systems.



